Overview¶
What is GPULab?¶
GPULab is a distributed system for running jobs in GPU-enabled Docker-containers. GPULab consists out of a set of heterogeneous clusters, each with their own characteristics (GPU model, CPU speed, memory, bus speed, …), allowing you to select the most appropriate hardware. Each job runs isolated within a Docker containers with dedicated CPU’s, GPU’s and memory for maximum performance.
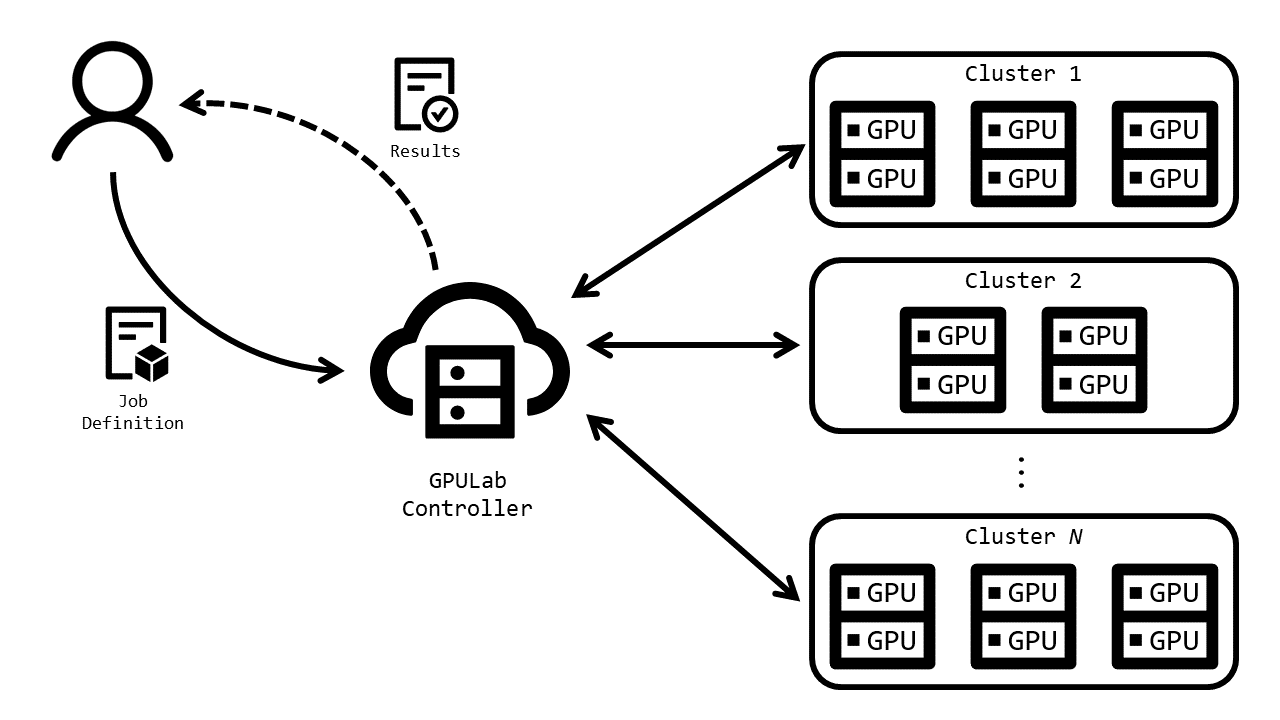
Users submit a job definition to the GPULab controller via a CLI or Web-interface. The job definition contains a reference to hardware being requested, the Docker image to be used, the command to be executed, the storage to be mounted, etc. The GPULab controller will then schedule this job as soon as possible on one of the appropriate slaves. Typically execution is instantaneous, but a job can be queued during busy periods.
All slaves have access to the same shared project storage which is also available to nodes on the imec Virtual Wall 2, this allows you to seamlessly prepare your input dataset and extract your results via this storage.
Tip
Do you want to develop your experiment with the hardware capabilities provided by imec’s GPULab? Our JupyterHub-instance allows you to run an interactive Jupyter notebook-session with your choice of hardware.
Once you’ve prepared your experiment you can submit your long-running non-interactive computations directly as GPULab jobs.
GPULab Clusters¶
GPULab consists out of a set of heterogeneous clusters which each contain one or more slaves (=bare metal servers). Within one cluster all slaves have the same characteristics in terms of GPU model, CPU speed, memory, bus speed, etc.
Example cluster configurations include:
- 3 slaves with 11 nVidia GeForce GTX 1080 Ti GPU’s, 32 1.8Ghz vCPU cores with 250GB RAM.
- 1 nVidia HGX-2 with 16 nVidia Tesla V100 GPU’s, 96 2.7Ghz vCPU cores with 1.5TB RAM.
- 1 slave with 1 nVidia GeForce RTX 2080 Ti GPU, 12 vGPU cores with 32GB RAM.
An up-to-date overview with the corresponding cluster-id’s can be found at the
live overview or via the gpulab-cli clusters command.
Note
Recently added hardware is first rigorously tested in a staging environment. For an overview of the hardware
available there, go to the Staging hardware overview or use the
gpulab-cli --dev clusters command
GPULab User Interfaces¶
Web Interface¶
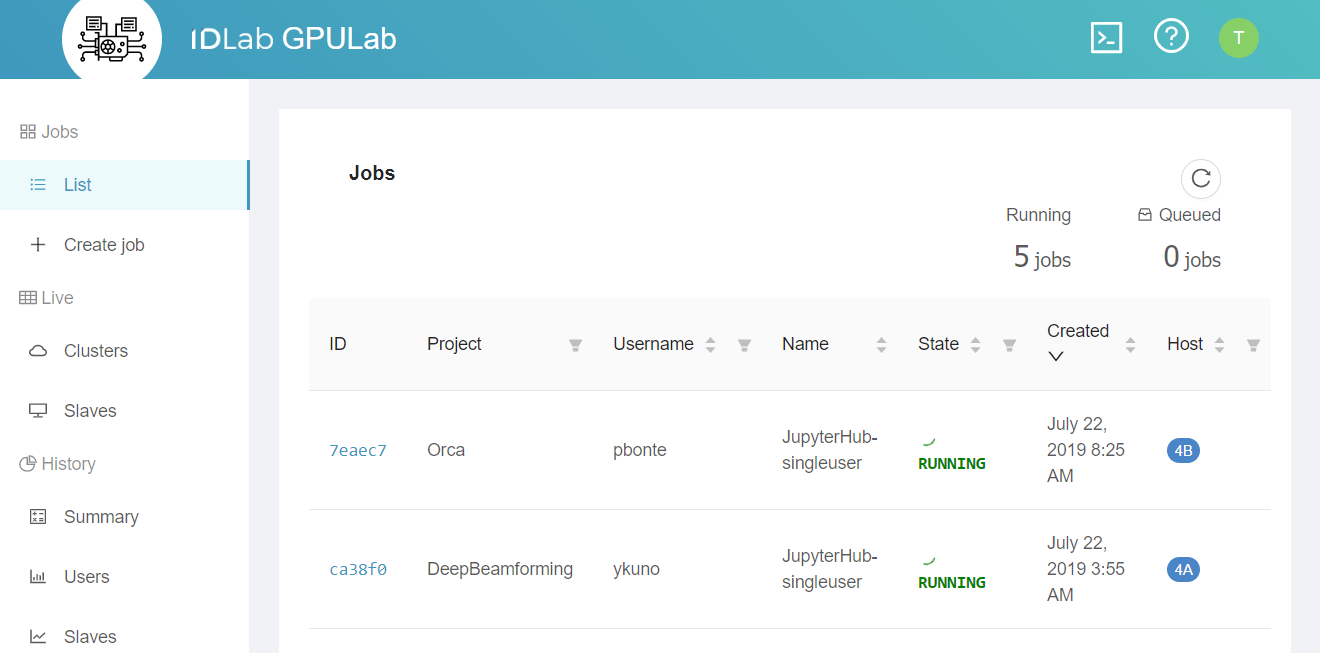
You can use most of the GPULab functionality directly from the GPULab Web Interface
Most users use this web interface to monitor their jobs, but they use the CLI to submit them.
Command Line Interface¶
GPULab offers an easy to use CLI interface. For most users this is the preferred way for submitting their GPULab jobs.
The CLI also allows you to retrieve the logs of a job, get console access to the running Docker container, etc. Use the
help-command for more information:
$ gpulab-cli --help
Usage: gpulab-cli [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
GPULab client version 1.9
Send bugreports, questions and feedback to: gpulab@ilabt.imec.be
Documentation: https://doc.ilabt.imec.be/ilabt-documentation/gpulab.html
Options:
--cert PATH Login certificate [required]
-p, --password TEXT Password associated with the login certificate
--dev Use the GPULab development environment
--servercert PATH The file containing the servers (self-signed)
certificate. Only required when the server uses a self
signed certificate.
--version Print the GPULab client version number and exit.
-h, --help Show this message and exit.
Commands:
cancel Cancel running job
clusters Retrieve info about the available clusters
debug Retrieve a job's debug info. (Do not rely on the presence or
format of this info. It will never be stable between versions. If
this has the only source o info you need, ask the developrs to
expose that info in a different way!)
hold Hold queued job(s). Status will change from QUEUED to ONHOLD
jobs Get info about one or more jobs
log Retrieve a job's log
release Release held job(s). Status will change from ONHOLD to QUEUED
rm Remove job
submit Submit a job request to run
wait Wait for a job to change state
GPULab API¶
For complex scenario’s, you can script the CLI. If this is not enough, you can directly use the GPULab API.

